Clinical investigations have pronounced that PEMF can help promote bone mineral density and reduce the fracture risks linked with osteoporosis.
An investigation directed in 2013 on beat electromagnetic field treatment demonstrated enhanced bone microstructure in rodents. The examination reasoned that PEMF has turned out to be a powerful noninvasive technique in the treatment of a wide scope of bone ailments. Their discoveries in the examination showed that 10-week utilization of PEMF astoundingly weakened the initiated bone misfortune and decay of bone small-scale design in rodents by advancing by and large quality articulations.
A treatment dialog about osteoporosis or osteopenia isn’t finished without considering the electromagnetic incitement of the bones. While nourishment, work out, hormone adjusting and supplements are basic to satisfactory bone development (especially post-menopause), they are frequently not enough. There are numerous conditions where these methodologies are deficient or unrealistic; notwithstanding when these techniques are reasonable, including electromagnetic incitement upgrades the potential advantages and long haul results. This implies different methodologies are important to manage osteoporosis/osteopenia satisfactorily.
Considerable research and proof are being amassed concerning the utilization of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) treatment in simultaneousness with osteoporosis.
It has PROVEN to be the only NONINVASIVE method capable of producing substantial therapeutic effects on bone diseased patients.
Several studies have demonstrated that PEMF can stimulate and promote osteogenesis, stimulate osteoblast activity and enhance bone mineralization.
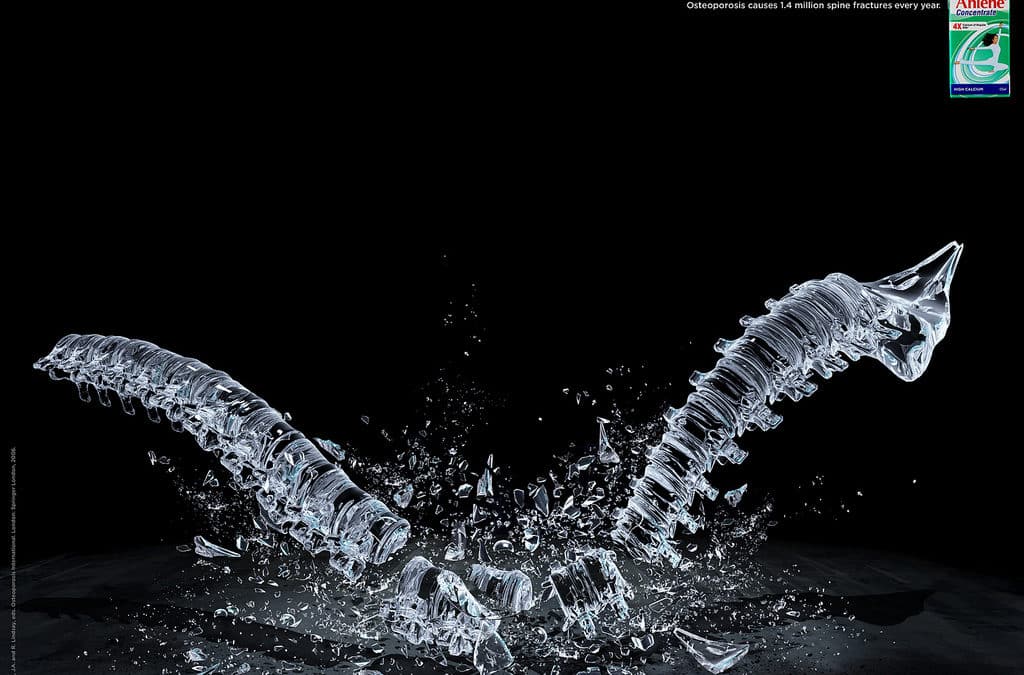
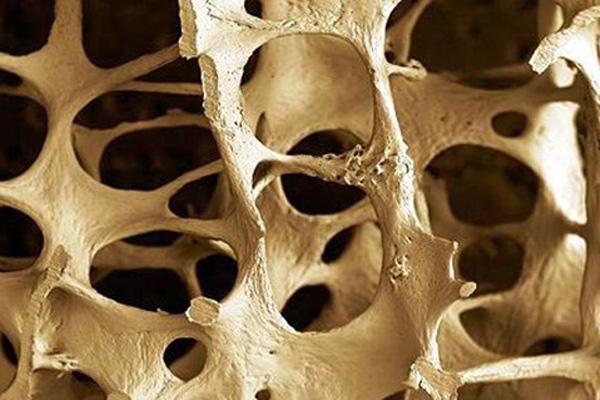
Globally, osteoporosis causes more than 8.9 million fractures per annum. To put this into perspective, every three seconds an osteoporotic fracture occurs. Osteoporosis is one of the most common conditions faced by the aging population, is characterized by a significant loss of bone mass and bone deterioration. Fragile bones significantly increase the risk of fractures. Osteoporosis has led to huge economic and socioeconomic impacts both in developing and developed countries. One in three women and one in five men over the age of fifty are expected to suffer a fracture caused by weak bones. Musculoskeletal diseases cause pain, disability, a loss of independence and premature death.
Another investigation directed could prompt the multiplication and separation of osteoblasts. The investigation utilized refined cells (MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts go 2012 exhibited that PEMF ct from a mouse) and presented them to PEMF for 30 minutes of the day for 2 days. The investigation was additionally done related to dexamethasone which is a glucocorticoid known to initiate osteoporosis by means of the prescription. The consequences of the examination demonstrated that PEMF treated osteoblasts demonstrated a noteworthy increment in multiplication and separation. The dexamethasone altogether diminished the expansion and separation impacts of PEMF.
The natural procedure of osteogenesis is known as bone renovating. At the cell level, bones are rebuilt through a sorted out process. Osteoclasts expel old bone and osteoblasts supplant it with recently framed bone.
Yale University School of Medicine studied the use of PEMFs in arthritis, but also found that they could be useful in the treatment of other bone disorders, including osteoporosis.
One researcher who helped develop an FDA-approved bone healing device showed that PEMFs had a profound effect on a large variety of biological systems, especially bone.
An orthopedic research team at Brown University found many therapeutic effects of electric and magnetic fields in the repair of connective tissue. (Bone is considered it a connective tissue.) The most widely studied applications are for bone repair and acceleration of the healing of fresh fractures, delayed and non-unions, incorporation of bone grafts, osteoporosis, and osteonecrosis. These fields even improve repair of cartilage and soft fibrous tissues. Basically, PEMFs accelerate extracellular matrix synthesis and tissue healing. PEMFs repair bone fractures non-union and enhances bone tissue formation, through enhancement of the formation of calcium phosphate crystal seeds in the bone.
Stress fractures are a common injury in athletes. They are most commonly seen in the lower extremities, especially with running. Stress fractures result from repetitive, cyclic loading of bone which overwhelms the reparative ability of the skeletal system. Typical treatment options include rest and stopping the activity. Some stress fractures are at risk for complications of healing. Women are more likely to have stress fractures. They are often related to eating disorders, amenorrhea, and osteoporosis, or the female athlete triad. PEMFs in this situation can be very helpful in both treatment and prevention.
The outcome
PEMFs have been shown in a wide variety of research to help bone repair and recover after injury, and also to prevent and treat osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Long-term entire body treatment is suggested. Osteopenia/osteoporosis are not simply restricted to the hip and spine. Bone mineral thickness testing is ordinarily just done on the lumbar spine and the hip. Clearly, osteopenia/osteoporosis include the whole skeleton with an expanded danger of breaks anyplace in the body, not simply the spine and hip.
PEMFs can’t be depended upon as a sole treatment. They should be joined with sufficient nourishment, enhancements, work out, and legitimate hormone adjusting or substitution. I have a few patients who have exhibited positive effects on their bones utilizing these mixes of treatment and without the need to depend on medications like Fosamax.
RESEARCH:
Jing, D., Li, F., Jiang, M., Cai, J., Wu, Y., Xie, K., … Luo, E. (2013). Pulsed electromagnetic fields improve bone microstructure and strength in ovariectomized rats through a Wnt/Lrp5/??-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. PLoS ONE, 8(11).
Esmail, M. Y., Sun, L., Yu, L., Xu, H., Shi, L., & Zhang, J. (2012). Effects of PEMF and glucocorticoids on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 31(4), 375–81.